-Assets (USD)
-Current Assets (USD)
-US Bank (USD)
-European Bank (EUR)
-HK Bank (HKD)
-Equity (USD)
-Opening Balances (USD)
-USD (USD)
-EUR (EUR)
-HKD (HKD)
Note: the currency of each account is shown in parenthesis.
Multiple Currencies
This chapter will show how to set up GnuCash accounts to use multiple currencies.
Basic Concepts
GnuCash supports over a hundred currencies, from the Andorran Franc to the Zimbabwe Dollar. For example, you can have a bank account set up in Euros, and another using Hong Kong Dollars.
Some of the issues which arise when using multiple currencies are, how do you transfer funds between accounts with different currencies? How do you calculate the overall value when you have mixed currency accounts? How do reports deal with mixed currencies?
|
Note
|
An alternative way to manage multiple currency accounts from the one presented in the next sections, is to use the trading accounts capabilities of GnuCash. This feature, which was introduced with GnuCash version 2.3.14, can be enabled by going to the Accounts tab under menu:File[ Properties]. For a complete guide on trading accounts, see this tutorial by Peter Selinger. |
Account Setup
Your default account currency is set in the Account tab under menu:Edit[Preferences] (menu:GnuCash[Preferences] on Mac OS X).
Similarly, GnuCash offers an option to set your preferred currency for displaying reports (like the balance sheet and income statement). The option is called Default Report Currency, and is in the Reports tab of the GnuCash Preferences screen. You’ll want to set both options when you start using GnuCash because if (for example) your accounts are all in Canadian Dollars but the generated reports are all in US Dollars, the reports will just say that there are "no data/transactions (or only zeroes) for the selected time period".
When you create a new account, you have the option to define the commodity in which that account is denominated. For accounts denominated in a currency, you can specify any of the currencies supported by GnuCash by simply selecting it from the currency commodity list. You will notice that the default currency is the currency that is defined for the parent account of the new account.
As an example, let’s set up a bank account scenario where you mostly work in US Dollars, but do also have a European bank account using the Euro currency, as well as one bank account in Hong Kong using Hong Kong Dollars. So, set up 3 bank accounts, one denominated in US Dollars, one using Euros, and the third in Hong Kong Dollars. One possible account structure for this would be:
Since in this example you mostly work in USD, all of the parent accounts are set to USD. Of course, if you mostly work in Euros, you could change the currency of these parent accounts to EUR. The totals shown in the account tree window will always be converted to the currency of each particular account. Notice, we also set up 3 Starting Balances equity accounts, used to initially populate the 3 banks.
|
Note
|
You could also set up just a single Starting Balance account and use a currency transfer to populate the "different currency" accounts. However, this is more advanced option, which is explained in a later section (Purchase of an Asset with Foreign Currency). |
Below you see the result of this example, in which you start with USD 10,000, EUR 10,000 as well as HKD 10,000 in the three bank accounts. Notice that the total of the parent accounts only shows the value of the currency of sub-accounts with matching currencies. In other words, the Total Assets and Total Equity values only reflect USD amounts, because GnuCash has no way of evaluating the value of EUR or HKD yet. Once you set up exchange rates between the currencies, the parent accounts will calculate the converted value of all sub-accounts. See the later section (Recording and Updating Currency Exchange Rates) on ways to do this.
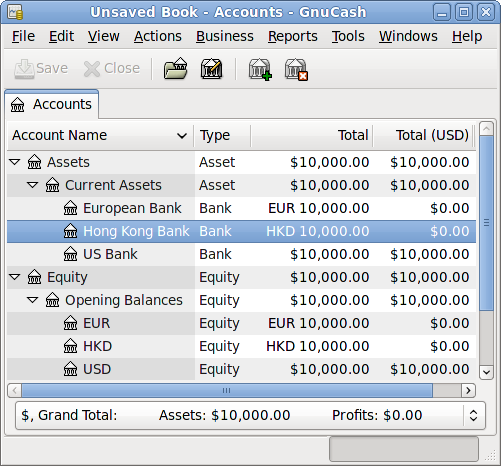
Notice that the "Total (Report)" column is being displayed. This is configured in the column header row, select Arrow down and select "Total(USD)".
User-Defined Currencies
Usually when we talk about currencies, we mean government-backed currencies (or more precisely, currencies defined in ISO 4217). GnuCash does not allow you to create your own currencies. If you want to track non-ISO currencies, you can use either of two workarounds, depending on which fits your needs better.
The first method is is to treat these as if they were a security—that is, like a stock or mutual fund. The second method is to use one of the "dummy" currencies for them.
Let’s say for example that you want to track loyalty points you’ve earned by buying from a certain group of businesses. The account which tracks your loyalty points will be Assets:Other:LoyaltyGroupRewardMiles.
In the first method, you define a new security, of type FUND, called RewardMiles. This is pretty straightforward—when you create the new LoyaltyGroupRewardMiles account, just set the account type to Stock or Mutual Fund, click the Select… button next to the Security/currency: box, and click New to define a new security of type FUND.
This is not really what the stock and mutual fund account types are meant for, but GnuCash will allow it. The downside is that you’ll have to enter a "price" for every transaction involving this account, because GnuCash needs the prices to figure out the monetary value of the points and treat them as one of your assets.
In the second method, you use one of the dummy currencies to track the loyalty points. These currencies are "XTS (Code for testing purposes)" and "XXX (No currency)". If you use one of these for your LoyaltyGroupRewardMiles account, you can enter transactions into the account without having to enter share prices for every transaction. And, you can keep using the same two dummy currencies to track all sorts of amounts—vacation dollars earned and used so far this year, vacation hours earned and used, health insurance benefits allowance used and remaining, and so on.
The drawback with this second method is that you cannot define exchange rates for the dummy currencies to convert them to ISO currencies. If you want to do that, you really should use the first method.
Recording and Updating Currency Exchange Rates
GnuCash allows you to update the Currency Exchange Rates both manually and automatically. This process is essentially the same as setting share prices for investments (see [invest-stockprice1]). In the following two sections we will work through both methods.
Before we start, let’s have a quick look at the Chart of Accounts

As you see, the overall balances do not yet reflect any value for EUR or HKD holdings. Adding currency exchange rates will fix this.
Manually Updating Exchange Rates
Open the Price Editor by going to menu:Tools[Price Editor].
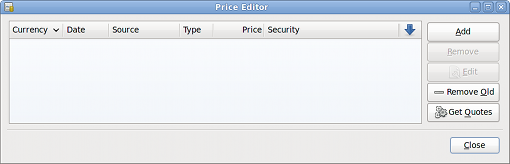
Click on the Add button to add a new currency exchange rate. A window will appear in which you can set up a new exchange rate. This window should appear like this:
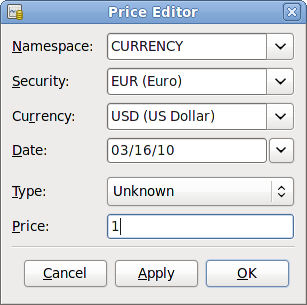
Set the Namespace to Currency and the Security to EUR (Euro). Then set the exchange rate between the selected security and the selected currency. The price box defines how many units of currency are required to purchase one unit of the security. In this case, how many dollars it will take to purchase on Euro. In this example, you will set the exchange rate to 1 EUR for 1 USD.
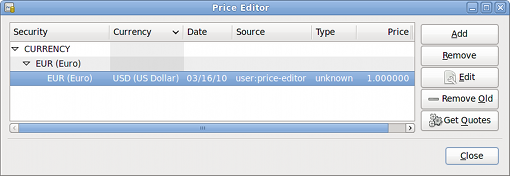
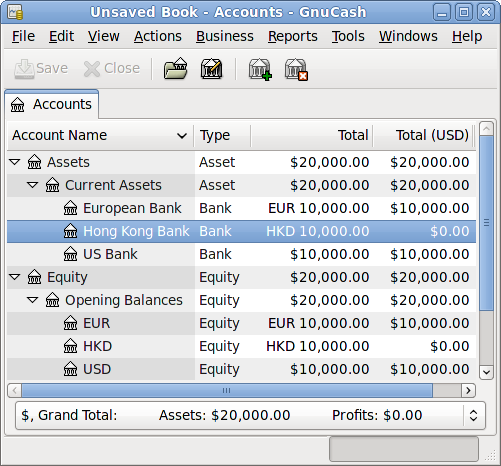
Observe that since you have no exchange rate for HKD, GnuCash doesn’t convert the HKD accounts to USD. This will be added in the next section.
Automatic Updating Exchange Rates (How-To)
In the previous section you saw how to manually define a new currency exchange rate, but GnuCash includes an automatic price update feature, which will now be described.
Open the Price Editor by going to menu:Tools[Price Editor].

Click on the Get Quotes button to automatically load the various exchange rates you need.
|
Note
|
If the Get Quotes button is disabled, that means that the Perl module Finance::Quote is not installed. For information on how to install it, please see [invest-stockprice-auto2] |
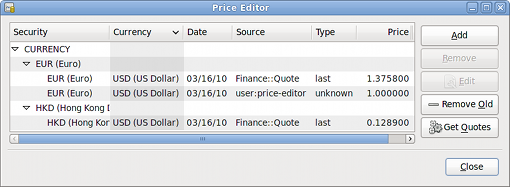
GnuCash downloads exchange rates for all currencies that are in use in your various accounts. This will happen every time you click on Get Quotes or request GnuCash to download quotes as per [invest-stockprice-auto2]
Now when you check the main Chart of Accounts you will see that GnuCash has automatically converted the HKD amount to USD amount on the parent accounts that are in USD, as well as on the Total (USD) column. Also the Euro accounts have been been updated with the latest exchange rate.
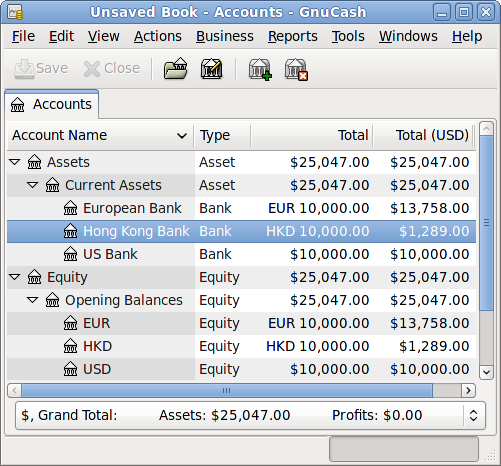
Disabling Exchange Rate Retrieval
Whenever you create an account that uses a non-default currency, exchange rate retrieval will be automatically enabled for that currency. However, if you later delete that account, GnuCash will not automatically disable exchange rate retrieval for that currency.
If you have deleted the last account for a particular currency, and you do not wish to retrieve exchange rates for that currency anymore, do the following:
-
Open the Securities window by selecting menu:Tools[Security Editor].
-
Make sure the Show National Currencies box is selected.
-
Expand the CURRENCY row.
-
Double click on the currency for which you want to disable exchange rate retrieval.
-
Deselect the Get Online Quotes box and click OK.
Recording Purchases in a Foreign Currency
Purchases in a foreign currency can be managed in two different ways.
1) Use GnuCash’s built-in currency exchange functions when you do your transactions. This is mainly used for one-time transactions, and nothing which happens regularly.
2) Use separate accounts to track transactions, where all involved accounts use the same currency. This is the recommended method, since it allows much better tracking and follow up. In this way, you do one currency exchange transaction, and after that you do normal transactions in the native currency.
The rest of this section will explain more based upon option 2).
Purchase of an Asset with Foreign Currency
You are using USD as your default currency. But, you decide to purchase a boat in Jamaica. To do this, you opened a bank account in Jamaica, moved some money from the US, and then purchased your boat.
To record this in GnuCash we use the following basic account structure:
-Assets (USD)
-Current Assets (USD)
-US Bank (USD)
-Jamaican Bank (JMD)
-Fixed Assets (USD)
-Boat (JMD)
-Equity (USD)
-Opening Balances (USD)
-USD (USD)
Note: the currency of each account is shown in parenthesis.
First you need to transfer some money ($10,000) to Jamaica, and you use your US bank account (with a balance of $100,000) for that. The bank gives you an exchange rate of USD 1 = JMD 64, but charges you USD 150 to transfer the money.
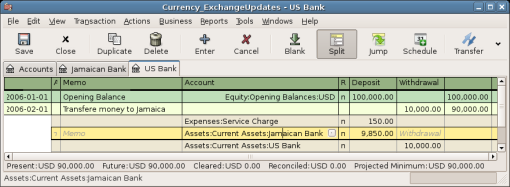
Select the Jamaica transaction line ($9,850.00), right click and select Edit Exchange Rate
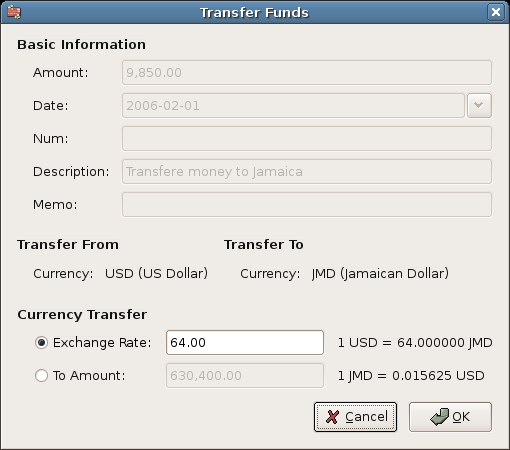
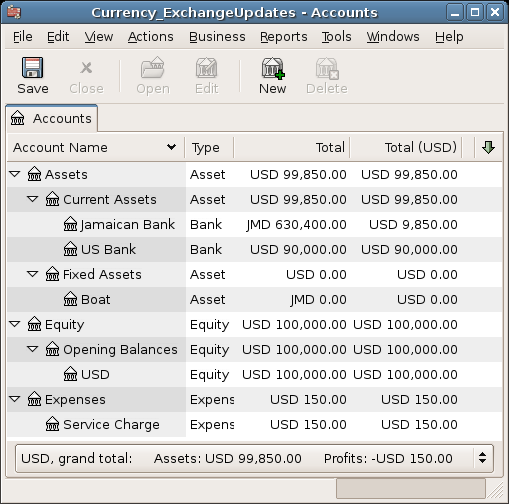
As Exchange Rate, you enter 1 USD = 64 JMD, since this is the rate your bank gave. Press ok in the Transfer Funds (Edit Exchange Rate) window, and then save this split transaction. Below is how it now looks in the main Chart of Accounts.
You choose to buy a boat for JMD 509,000. To record this transaction in GnuCash, you will need to enter a simple transaction in Assets:Current Assets:Jamaican Bank withdrawing JMD 509,000 and transferring it to Assets:Fixed Assets:Boat
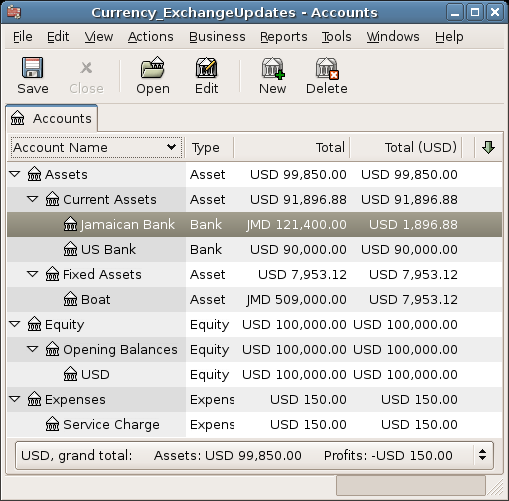
The Chart of Accounts now reflects that your bank account has been reduced by JMD 509,000, and that your Fixed Assets boat account has been increased by the same amount. If you also have turned on the CoA (Column Choice) "Total (USD)" you will see the corresponding value in USD. The USD value will always reflect the latest currency exchange rate you have either automatically or manually retrieved.
Purchasing Foreign Stocks
This example will show how to purchase stocks that are priced in a currency other than your primary currency.
Assume that you live in New York and therefore you have set the default currency to USD. You decide to purchase a stock traded in Hong Kong that is priced in HKD. You would also like to be able to track the various income and expense amounts per stock and broker.
You decide to purchase stock in the Beijing Airport (Hong Kong). The ticker for this stock is 0694.HK on Yahoo! Since you wanted to track all various income and expense amounts, here is the necessary account structure:
Assets:Investments:Brokerage Accounts:Boom:0694.HK (0694.HK) Assets:Investments:Brokerage Accounts:Boom:Bank (HKD) Equity:Opening Balances:HKD (HKD) Expenses:Commissions:Boom.0694.HK (HKD) Income:Investments:Dividend:Boom:0694.HK (HKD)
The Chart of Accounts looks like this after creating all the needed accounts:
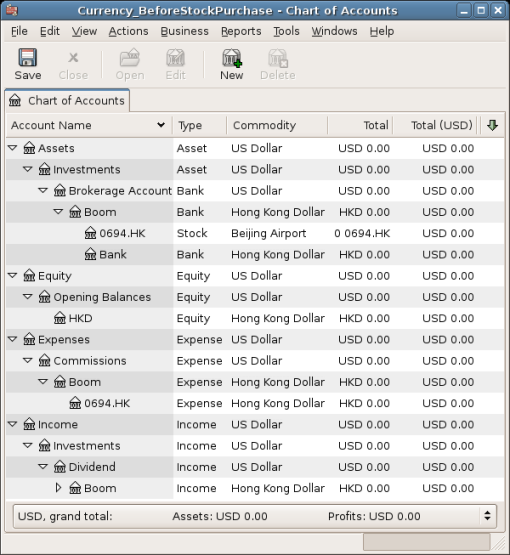
The stock definition can be seen in the Security Editor. (menu:ToolsSecurity Editor[])
If you have not moved money (HKD 50,000) into the brokerage cash account (Assets:Investments:Brokerage Account:Boom:Bank), do so now, either using the Equity (HKD) account, or an existing bank account (Currency Transfer).
There are two ways to enter the actual purchase transaction: you can enter it from the cash account (shown below), or you can enter it from the stock account. If entered from the stock account, the stock is assumed to be priced in the currency of the parent account.
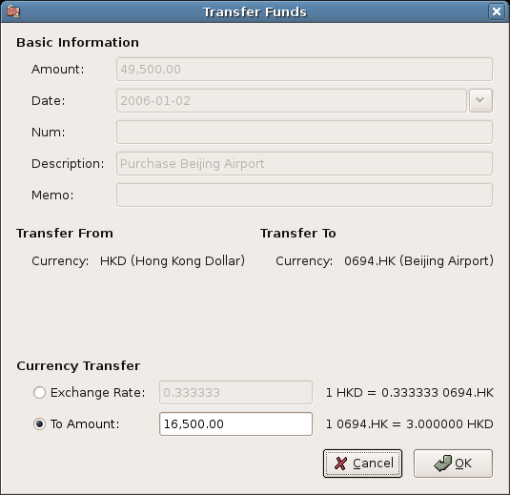
Let’s assume that the stock price is HKD 3 per share. To record the purchase, open the brokerage’s HKD cash account (Assets:Investments:Brokerage Account:Boom:Bank), and enter the following:
Buy Stocks
Assets:Investments:Brokerage Account:Boom:Bank |
Withdrawal |
50,000 |
Expenses:Investments:Commission:Boom_HKD |
Deposit |
500 |
Assets:Investments:Brokerage Account:Boom:0694 |
Deposit |
49,500 (16,500 shares) |
If the exchange rate dialog box does not appear automatically, right-click on the stock row, and select Edit Exchange Rate. Enter the number of shares (16,500) as the To Amount.
When you return to the Chart of Accounts, you will see the purchased shares reflected in the stock account’s total.
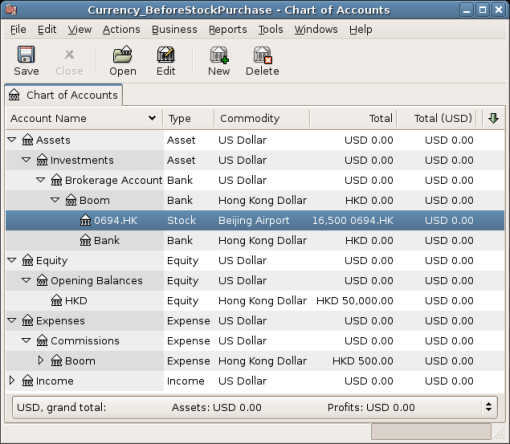
However, as you can see, the USD totals may be zero if GnuCash doesn’t have an exchange rate between USD and HKD. To fix this, go to menu:Tools[Price Editor] and click the Get Quotes button to automatically retrieve the exchange rates you need.
|
Note
|
To reiterate, this example shows how stock can be purchased in any currency by entering the transaction in the register of the cash account used to make payment. It is also possible to enter the purchase in the stock account’s register, but be aware that the stock is assumed to be priced in the currency of the stock account’s parent. In this example, the stock account’s parent (Assets:Investments:Brokerage Account:Boom) is denominated in HKD. Since this is same currency as the stock price, the purchase can be safely entered in the stock account’s register. |
Tracking Currency Investments
Currency investment is when you decide to invest in a different country’s currency, and hope that it will rise in value relative your own currency.
When you enter these transactions into GnuCash, you will have to decide on how much detail you would like to have.
If you are not interested in detail at all, a very simple account structure would suffice:
Assets:Investments:Currency:Bank (USD)
Assets:Investments:Currency:XXX (XXX)
You would simply enter transfers between the two accounts, noting exchange rates as you went.
But, if you do want to be able to track capital gains or losses, as well as any fees, you do need a more complex account structure, such as:
Assets:Investments:Currency:Bank (USD)
Assets:Investments:Currency:Currency Bank:XXX (XXX)
Expenses:Investments:Currency:Currency Bank:XXX (XXX)
Income:Investments:Currency Bank:Capital Gains:XXX (XXX)
Purchasing Currency
When purchasing another currency, you will buy a certain number of units of foreign currency with your own currency, at a particular rate. For example, you might buy USD 10,000 worth of Andorran Francs, at 5 Francs to the dollar, with a transaction fee of $150.
Buy Currency
Assets:Investments:Currency:Bank |
Withdrawal |
10,000 |
Expenses:Investments:Currency:Currency Bank:ADF |
Deposit |
150 |
Assets:Investments:Currency:ADF |
Deposit |
49,250 |
The Exchange Rate window should pop up when you leave the last row in the split above (Currency Transaction). If this window does not pop up, right click on the row or select , and select Edit Exchange Rate. In the Exchange Rate window you specify the exchange rate you got from the bank.
Selling a currency investment
Entering a currency sale is done in the same way as a currency buy except that you are now transferring money from the Currency account to your Savings account (very similar to [invest-sell1]).
The proper recording of the currency sale must account for realized gains or losses. This can be done using a split transaction. In the split transaction, you must account for the profit (or loss) as coming from an Income:Capital Gains account (or Expenses:Capital Loss). To balance this income, you will need to enter the Currency asset twice in the split—once to record the actual sale (using the correct amount and correct exchange rate), and once to balance the income profit (setting the amount to 0).
In short, a selling Currency transaction should look something like below, seen again from the Assets:Investments:Currency:Bank.
| Account | Deposit | Withdrawal |
|---|---|---|
Assets:Investments:Currency:Bank |
Sold Amount - Exchange Fee |
|
Expenses:Investments:Currency:Currency Bank:XXX |
Exchange Fee |
|
Assets:Investments:Currency:XXX |
Sold Amount |
|
Income:Investments:Currency Bank:Capital Gains:XXX |
[LOSS] |
PROFIT |
Assets:Investments:Currency:XXX |
PROFIT (with To Amount = 0) |
[LOSS (with To Amount = 0) ] |
Reconciling Statements in a Foreign Currency
Reconciling foreign statement are done in the same manner as when you reconcile your local bank statement. If you have created a Chart of Accounts structure which allows you to have the same currency per account as your statement, it is actually exactly the same as reconciling your local bank statement.
If you have different currencies you might have to manually convert the amounts from one currency to another while you reconcile the accounts.